GMOD
ParameciumDB

ParameciumDB (http://paramecium.cgm.cnrs-gif.fr) is a model organism database for the unicellular eukaryote Paramecium tetraurelia. ParameciumDB contains genome sequence and annotations, alleles and RNAi knockdowns, mutant phenotypes, and stocks all in a tightly integrated package. ParameciumDB is a good example of an online biological resource built mainly with GMOD Components.
This article provides an overview of Paramecium followed by a description of how ParameciumDB was implemented using GMOD components.
The intent of this page is to give you a feeling for how ParameciumDB uses GMOD, and what challenges they faced.
See also:
- ParameciumDB website:
- ParameciumDB: a community resource that integrates the Paramecium tetraurelia genome sequence with genetic data, in the January 2007 Database Issue of Nucleic Acids Research.
Contents
- 1 Paramecium Biology
- 2 ParameciumDB
- 3 Implementation
- 4 Related Reading
Paramecium Biology
Paramecium is a unicellular eukaryote that belongs to the ciliate phylum. Ciliates are the only unicellular organisms that separate germinal and somatic functions. Diploid but silent micronuclei undergo meiosis and transmit the genetic information to the next sexual generation. Highly polyploid macronuclei express the genetic information but develop anew at each sexual generation, through extensive programmed rearrangements of the genome.
Paramecium is a model for studying
- complex functions characteristic of multi-cellular organisms
- somatic differentiation involving programmed rearrangements of the genome at each sexual generation
- biogenesis of cilia and ciliary basal bodies (equivalent to centrioles)
- regulated secretion
- receptor- and ion channel-mediated cell signaling in response to environmental stimuli
- cytoplasmic non-Mendelian heredity and underlying homology-dependent
mechanisms that involve non-coding RNA
- mating type and other characters are inherited maternally
- cortical pattern: related to prion heredity
- evolutionary consequences of whole genome duplication
- at least 3 whole genome duplications and an unprecedented number of paralogs related by whole genome duplication
- explosive speciation followed the most recent whole genome duplication (15 sibling species of the P aurelia complex)
- dosage constraints seem to shape the gene repertoire
Paramecium tetraurelia Genome
The somatic genome has been sequenced by Genoscope using a whole genome shotgun approach. That assembly and subsequent analysis have resulted in:
- 72 Mb assembly
- 39,642 gene models, with an average of 2.3 introns per gene
- 12,026 paralog pairs from most recent whole genome duplication
ParameciumDB
ParameciumDB is maintained by two people, Linda Sperling and Olivier Arnaiz at the Centre de Genetique Moleculaire, a part of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. ParameciumDB is mainly implemented with GMOD Components.
ParameciumDB is first came online in August 2005.
Implementation
This section covers some details of how ParameciumDB was implemented and how it is maintained. This focuses on how GMOD Components are implemented, but also touches on toher technologies as well.
See also:
- Setting up ParameciumDB in Scott Cain’s presentation at the May 2005 GMOD Meeting.
- About ParameciumDB on the ParameciumDB web site.
Database
ParameciumDB is built on the Chado schema and implemented in PostgreSQL database management system.
Design Overview
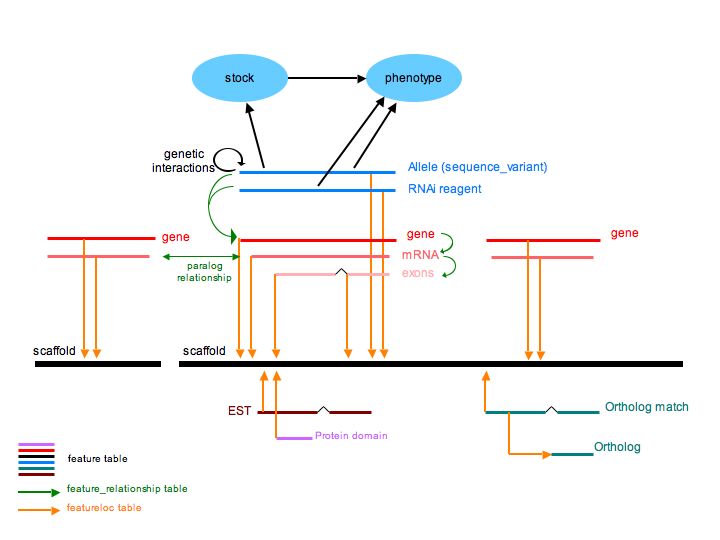
Chado Modules
ParameciumDB uses core Chado modules, plus the Genetic and Stock modules.
General Module
ParameciumDB uses the Chado General Module to handle database IDs and cross-references.
Pub Module
The Chado Publication Module is another core Chado module. ParameciumDB does not manually curate publications, but they do mine PubMed entries for Paramecium allele references.
Sequence Module
The Chado Sequence
Module, another core
module, is used to represent sequence features and
synteny.
Because of the recent whole genome duplication, a great deal of thought
has been given to how to represent paralogy and synteny. These are
represented in the sequence module using the feature, featureloc, and
feature_relationship tables.
See also:
- Synteny data in ParameciumDB working document
Controlled Vocabulary Module
The core Chado CV Module is used to store these ontologies:
- Sequence Ontology (SO)
- Gene Ontology (GO)
- Relation Ontology (RO)
- Phenotype and Trait Ontology (PATO)
- Paramecium Anatomy Ontology
- Paramecium Assay Ontology
The last two were developed at ParameciumDB to enable phenotypes to be modeled using the Entity-Quality model. The quality terms are provided by PATO. The anatomy ontology was developed for the Entity terms, since more granular ‘cellular component’ terms than are available in GO were needed to describe some species- or phylum-specific traits and cytological features, such as nuclear dimorphism and the ciliate cortex.
Ultimately, the ciliate- and Paramecium-specific terms in the Paramecium Anatomy Ontology, will be proposed for integration into the GO Cell Component Ontology. This still requires more work on the definitions and on identification of the appropriate place for the new terms in the GO Cell Component hierarchy.
The assay ontology will hopefully also be incorporated into a broader assay ontology in the future.
To create new phenotypes, we use the Phenote tool.
Genetic Module
This Chado Genetic Module is used to model information about Paramecium alleles, genetic interactions and phenotypes.
The genetic module is tightly linked to the Stock Module.
Stock Module
The Chado Stock Module, which is now a standard Chado extension module, originated at ParameciumDB.
This module was necessary to allow integration of Paramecium Stock Collections into ParameciumDB.
Web Site
Turnkey / GMODWeb
ParameciumDB uses Turnkey, a generic Web framework built on Apache, mod_perl, and SQLFairy, that takes a relational schema of a given database as input and transforms it into a fully-functional and customizable web site within minutes. We use templates and cascading style sheets to customize the ParameciumDB web interface.
GBrowse
GBrowse, the Generic Genome Browser, is used to display and query sequence annotation with a Bio::DB::SeqFeature::Store database.
Annotation
ParameciumDB does not have paid curators. It currently relies on the community for annotation of the gene models. They use Apollo as their genome annotation editor.
See also:
- Community Annotation Project from ParameciumDB web site
- Community Annotation at ParameciumDB - Linda Sperling’s presentation at the November 2007 GMOD Meeting.
Middleware
Bio::Chado API
The Bio::Chado API is Perl Category%253Amiddleware module for working with Chado databases. It was developed specifically for the BioPipe project (so that BioPipe users can choose to store pipeline results in a Chado database as opposed to an EnsEMBL database) and for ParameciumDB.
Comments
Issues
- Content control - moved to CVS
- Incorporation of the custom Chado Stock Module
- Getting Turnkey/GMODWeb to work
- Logical Chado issues
- Making all features part-of chromosome
- Making results children of genes
- GBrowse Chado adapter bugs
- Getting parsers and loaders bug free.
- Making Apollo and Chado data models compatible
- Maintenance of data, schema and new software versions
Feedback
- GBrowse documentation is very good for Bio::DB::GFF but a little less so for Bio::DB::Das::Chado.
- Chado’s install documentation is not bad but requires investment.
- Turnkey is a wonderful tool and it should continue to be developed.
- Apollo is a beautiful genome editor, though it is complicated for a naive user.
- BioMart seems to be a very powerful tool and is an invaluable addition to any MOD.
- Chado Mage Module is being successfully used for transcriptome data, but it is not yet visible to the public.
Related Reading
- ParameciumDB website:
- ParameciumDB: a community resource that integrates the Paramecium tetraurelia genome sequence with genetic data, in the January 2007 Database Issue of Nucleic Acids Research.
- Scott Cain’s presentation (the “Setting up ParameciumDB” section) from the May 2005 GMOD Meeting.
- Community Annotation at ParameciumDB - Linda Sperling’s presentation at the November 2007 GMOD Meeting.
- Synteny data in ParameciumDB working document.